The function of the solenoid valve is to change the direction of the air circuit through the solenoid coil being energized or de-energized, so as to control the direction of action of the actuator. Solenoid valves can be divided into direct-acting and pilot-operated in terms of their action modes; in terms of the number of coils, they can be divided into single coil and double coil; in terms of the number of stations and interfaces, they can be divided into two three-way, five-way Three digits, five links, etc.
1) Principle
a. Direct-acting solenoid valve
When the solenoid coil is electrified, it produces magnetism. The magnetism acts as a power to push the valve core upward and the solenoid valve opens; when the solenoid coil is de-energized, the spring pushes the valve core downward and the solenoid valve closes.
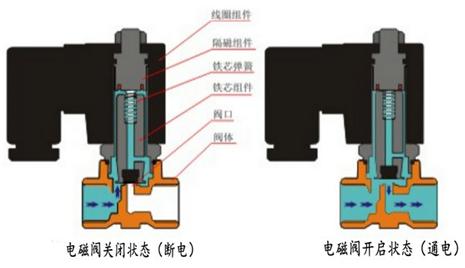
Internal principle diagram of direct-acting solenoid valve
b. Pilot solenoid valve
The internal principle diagram of the pilot solenoid valve is shown in Figure-4, 1 is the air inlet, 2 is the air outlet (normally open), and 4 is the air outlet (normally closed). 3 and 5 are vent holes. After the coil is electrified, pull the small valve core to move to the right. After the small valve core is opened, high-pressure gas enters the right side of the piston, and the pressure gradually increases. When the left side pressure is open to atmosphere, the unbalanced force compresses the large spring and pushes the piston and the slider to the right. Move to the left, this position is 1 and 4 ports (intake), 2 and 3 ports (exhaust). When the solenoid valve is de-energized, the small spring pushes it to move to the left, the small valve core is closed, the pressure on the left side of the piston is reduced to zero, and the slider moves to the right to the position shown in Figure-4 by the large spring. This position is 1 and 2 ports (in Gas), 4 and 5 ports (exhaust).
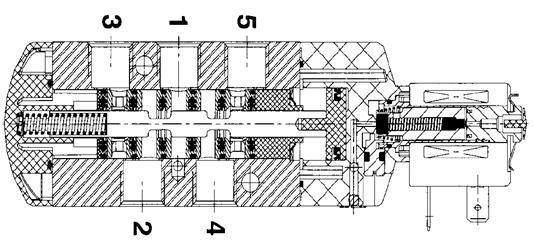
![]()
The internal principle diagram of the pilot solenoid valve
2) Advantages and disadvantages
a. Direct-acting solenoid valve: fast response speed, not affected by air pressure; small flow capacity, high power, and large heat generation.
b. Pilot solenoid valve: large flow capacity, low power, low heat generation; response speed is slightly slower than direct-acting type, when the intake pressure is lower than 2Bar, the solenoid valve cannot operate.
3) How to choose correctly
a. Direct-acting solenoid valve: used in occasions where the valve opening and closing time is not high; it controls the gas signal of the pneumatic reversing valve to realize the function of fast switching and not limited by the intake pressure; installed in the positioner output gas circuit, Realize the function of opening or closing the power-off valve.
b. Pilot solenoid valve: directly installed in the on-off valve pipeline to realize fast switching function; control pneumatic reversing valve gas signal to realize fast switching function.